Toyota’s Solid State Battery Finally Hit The Market
What are the top five most important components of an electric car? For many people, the battery will come in the top two and won’t be second.
The battery is required because that is where the energy to move the car comes from. The EV industry has settled for the lithium-ion battery, but the battery has several drawbacks that do affect EV performance.

Many car makers are in a race to make the best battery to beat the competition. One of those leading the race is Toyota, whose solid-state battery has finally hit the market.
What is a solid-state battery?
How far has Toyota come in developing its breakthrough?
In this article, we bring you Toyota solid-state battery that is finally hitting the market. If you take delivery of a battery electric vehicle today, you will most likely get a lithium-ion battery.
Lithium-ion batteries become so prevalent in today’s technologies that you find them everywhere. Your phone uses lithium-ion batteries the same as your laptop and many other gadgets that you might not even think of right now.
Lithium-ion batteries were a massive improvement over lead-acid batteries, and this is most evident in the electric car industry.
Before, Tesla showed the world what lithium-ion batteries can do by putting them in its first car, the Roadster. Electric vehicles were severely limited in range, making them impractical.
However, the Roadster showed everyone that an electric car, especially a high-performance one, could last more than 200 miles before it needed to be charged.
Since then, the lithium-ion battery has seen lots of improvements, resulting in procurement going down. However, the lithium-ion battery has its own set of problems that hold back EVs.
Attempting to eliminate these issues is why battery scientists have been looking for the next big thing in the industry, and Toyota has found the very next big thing in batteries in the form of the solid-state battery.
What are the lithium-ion battery problems that Toyota wants to solve with the new solid-state battery?
It’s required to know to fully appreciate Toyota’s brilliant effort with a new battery. Lithium-ion requires higher protection.
- They need protection from overcharging to a great extent.
- Lithium-ion batteries require maintenance many times.
- Every lithium-ion battery needs protection.
That is a significant disadvantage. It adds weight and increases the complexity and the cost. It also makes recycling very difficult. The lithium-ion batteries also weigh a lot.
The battery can take up about one-third of the car’s weight. This makes the tires wear out more quickly.
The designers also have to balance the weight distribution in the car, something that complicates the development. Also, lithium-ion battery performance declines with time.
Even though lithium-ion battery life is long-lasting, it never remains the same throughout its lifespan.
The effectiveness and performance of lithium-ion batteries tend to decrease as time passes. In addition to this, lithium-ion batteries can also reduce their performance whether they are in use or not.
Notwithstanding the usage, there is also a time-related factor to the declining capacity. Another disadvantage of lithium-ion batteries is that they are not safe to use.
At higher temperatures, lithium-ion batteries can become explosive and catch fire. This risk increases when an EV is involved in a car crash.
On the other hand, cold temperatures negatively affect lithium-ion batteries.
The driving range drops significantly, especially where snow falls. For similar reasons, charging the battery takes longer in cold weather.
However, perhaps the biggest drawback of lithium batteries is the cost. These batteries are expensive because of the materials used, especially in the cathode.
Cobalt, nickel, and so forth cost a lot and the supply chain fluctuates, leading to volatile prices.
Battery prices are indeed falling, but they are still expensive. Enter the solid-state battery.
As mentioned before, Toyota is not the only company working on solid-state batteries.
For example- the same Samsung that makes the popular Galaxy line of phones is involved in solid-state batteries.
Quantum Scape is also into solid-state batteries and has raised more than 1 billion in funding. It is supported by more than 17 investors.
BrightVolt is another company deeply involved in solid-state battery development. Fiscal made a lot of noise about solid-state batteries but gave up the project.
However, none of these companies have been close to Toyota’s speed or have recorded as many breakthroughs.
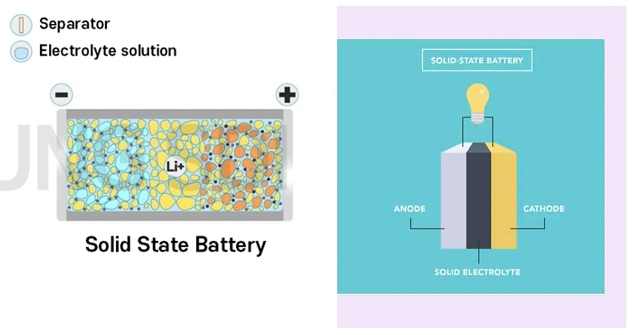
How does a solid-state battery work?
Surprisingly, solid-state batteries have a lot in common with standard lithium-ion batteries.
The only difference is that a solid-state battery consists of a solid electrolyte. In place of a liquid electrolyte, materials such as glass, ceramic and more can be used for this purpose.
A solid-state battery makes use of solid electrodes and solid electrolytes. Solid electrolytes include oxides, sulfide phosphates, polyethers, polyesters, nitrile-based, polysiloxane, polyurethane, and more. The performance depends on the electrolyte used.
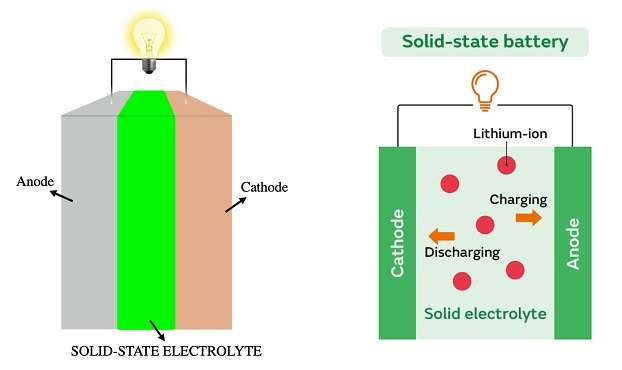
How solid state batteries work like lithium-ion batteries.
You have the anode and cathode made of electrically conductive materials. An electrolyte is present between the two electrodes.
The lithium ions move through the electrolyte that produces current. When the ions move from the cathode to the anode, that is, from the positive electrode to the negative electrode you are charging.
Similarly, the movement of ions in the reverse direction, that is, from the anode to the cathode, discharges the battery and supplies the current to the load.
What does Toyota’s solid-state battery offer?
Its offerings are numerous. Even though we told you the batteries are similar to standard lithium-ion batteries, solid-state batteries are capable of delivering two and a half times more energy density as compared to lithium-ion batteries.
That means for the same size battery size and mass, Toyota can significantly increase the driving range of its EVs.
Toyota could be on its way to the first EV with more than 10 miles of range. Solidstate batteries are comparatively more durable and safe.
That is because of the solid electrolyte used in solid-state batteries, which is non-flammable. Hence, they are less prone to catch fire.
Apart from these, solid-state batteries are comparatively less expensive and compact. In addition, solid-state batteries are comparatively lighter in weight.
Toyota’s cars will weigh less, allowing the battery to last even more miles on the road. Less mass means less energy consumed during operation.
The recharge rate of solid-state batteries is four to six times more than regular batteries.
That is an important advantage because one of the biggest complaints about EVs is the charging times. An average EV can take up to an hour to fully charge, and this could be a problem for drivers on longer trips who have to stop to refill the battery.
It is also a sticky point for fleet operators whose time is money. However, solid-state batteries will allow Toyota to make cars that can charge in under 10 minutes, which is not so bad compared to internal combustion engine cars.
How far has Toyota gone with its solid-state battery?
It’s left all others behind. The Japanese company already has a working prototype running completely on its solid-state battery.
You can see it is a version of Toyota’s LQ concept, which first debuted at the 2019 Tokyo Motor Show as an AI and self-driving demonstrator.
A static model, the prototype was filmed driving down its power. Toyota’s VP of Mobility Communications, Shiro Takimoto, explains that his company has obtained license plate registration for vehicles equipped with all-solid-state batteries and conducted test drives.
Toyota is already talking about the first cars to get the new solid-state battery.
In an interview with Gill Pratt, Toyota’s chief scientist and head of the Toyota Research Institute said that the first Toyotas to receive the new batteries would be hybrids instead of fully electric vehicles.
The company does have practical reasons for making the decision.
In a hybrid, the smaller battery is charged and recharged far more often, and perhaps suggested the increased amount of cycling for the batteries will make hybrids a good test bed for the new technology.
So the battery will get even better before it’s used in a BEV. That you might buy. Let’s hear what you think of Toyota’s new solid-state battery in the comments section below.
