Stellantis is taking a major step toward improving electric vehicle (EV) charging efficiency with a new hardware solution designed to increase power output from low-power DC fast chargers. By addressing limitations in current charging infrastructure, this development could make EV charging faster and more convenient, particularly for vehicles using 800-volt architectures like the upcoming Ram 1500 REV.
This innovative approach is detailed in a patent filed with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) on April 25, 2023, and published on October 31, 2024. While the patent doesn’t mention Tesla explicitly, it’s hard to ignore the implications for vehicles charging on Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network, which primarily uses a 400-volt system.

What’s the Problem Stellantis is Solving?
Most DC fast chargers, including Tesla’s widely available Supercharger network, operate on a 400-volt system. This setup can limit the charging speed for EVs equipped with advanced 800-volt architectures, which are capable of handling higher power. While dedicated DC boost modules can bridge this gap, they come with significant downsides:
- Added weight: Extra hardware increases the vehicle’s overall weight, impacting efficiency.
- Higher costs: Dedicated boost modules are expensive to produce and integrate.
- Complex packaging: Fitting these components into EV designs can be challenging.
Stellantis’ solution eliminates the need for bulky, expensive hardware, making it a more practical and efficient alternative.
How Does Stellantis’ Boost System Work?
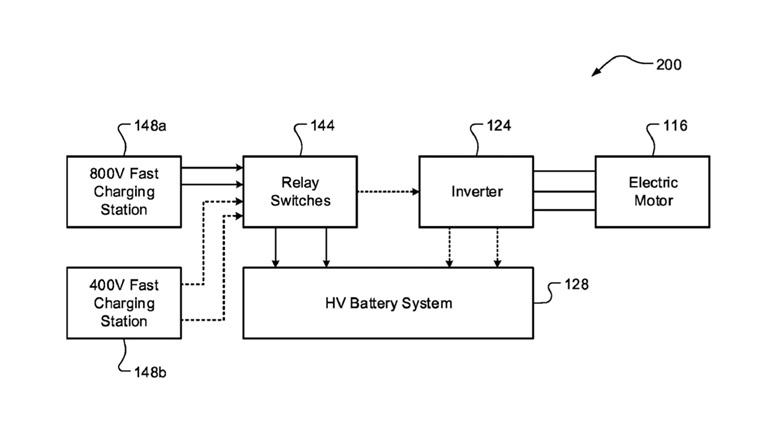
The proposed system uses a series of relay switches and a small DC capacitor to enhance the charging process. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Relay switches: These allow current to flow through the vehicle’s inverter and electric motor during charging.
- AC to DC conversion: The inverter and motor generate two alternating current (AC) phase currents.
- Boosted DC current: The AC currents are converted into a higher-power direct current (DC) that charges the battery more efficiently.
This method takes full advantage of an 800-volt vehicle’s capabilities, even when using 400-volt DC fast chargers.
Traditional Boost Modules vs. Stellantis’ Relay System
| Feature | Traditional Boost Modules | Stellantis’ Relay System |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Adds significant weight to the vehicle | Minimal added weight |
| Cost | High production and integration costs | Low-cost solution |
| Complexity | Challenging to package in vehicle designs | Compact and easy to integrate |
| Scalability | Limited to high-end models due to cost | Applicable across a range of EVs and PHEVs |
Why This Matters for 800-Volt EVs
800-volt systems are increasingly popular in larger EVs because they enable faster charging and improved energy efficiency. However, the lack of widespread 800-volt charging infrastructure has been a bottleneck. Stellantis’ relay-based solution bridges this gap, making it possible for 800-volt EVs to achieve higher charging rates even at 400-volt stations.
This innovation is particularly relevant as Stellantis adopts Tesla’s North American Charging Standard (NACS), which operates on 400 volts. By enabling faster charging on existing infrastructure, Stellantis could offer a smoother experience for EV drivers transitioning to its vehicles.
Who Will Benefit Most?
While the relay-based boost system may not immediately impact all Stellantis EVs, it holds great promise for future models, particularly:
- 800-Volt Vehicles: Like the Ram 1500 REV, which has been confirmed to feature 800-volt architecture.
- Plug-In Hybrids (PHEVs): The technology could also be applied to PHEVs, offering broader benefits across Stellantis’ lineup.
However, many of Stellantis’ upcoming EVs, including the Dodge Charger Daytona and Jeep Wagoneer S, will stick to a 400-volt architecture, making this innovation less immediately relevant for those models.
Looking Ahead: Stellantis’ Streamlined EV Strategy
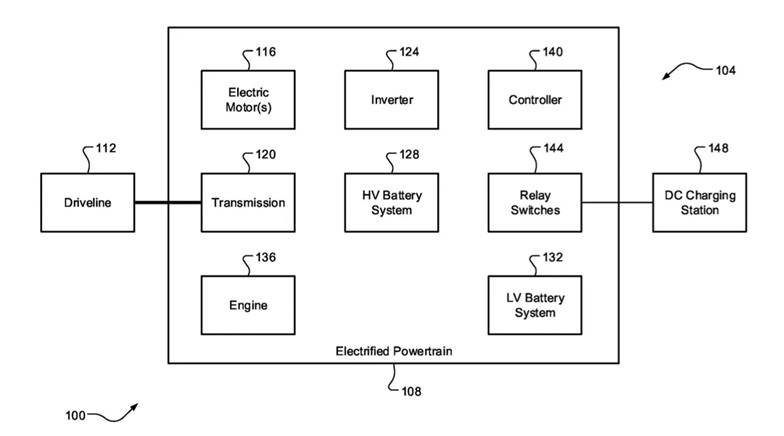
This charging boost system aligns with Stellantis’ broader strategy to simplify EV designs. In 2023, the automaker revealed plans to eliminate onboard chargers and inverters in some future models, further streamlining its EV architecture.
By reducing complexity, weight, and costs, Stellantis is positioning itself to offer competitive and efficient EVs that cater to a wide range of customers.
Stellantis’ relay-based charging solution represents a clever and cost-effective approach to a pressing issue in the EV industry. As more automakers transition to 800-volt architectures, the ability to maximize charging efficiency on existing 400-volt infrastructure will become increasingly important.
For consumers, this innovation promises faster and more flexible charging options, potentially making Stellantis EVs a more attractive choice in a competitive market. Whether you’re eyeing the upcoming Ram 1500 REV or simply interested in the future of EV technology, Stellantis’ forward-thinking approach could shape the way we charge and drive electric vehicles in the years to come.
Related Post
